Flexible and Blended Learning is an educational approach that integrates both traditional face-to-face instruction and online learning. It provides learners with the flexibility to access course materials and engage with instructors and peers through various platforms, allowing them to manage their learning according to their schedules and preferences.
Flexible and blended learning emerged as a response to the changing needs of learners in the digital age. It accommodates students who require learning environments that go beyond the constraints of the traditional classroom. The integration of technology allows for more personalized learning experiences, collaboration across different geographical locations, and the opportunity to balance education with other life commitments. This educational model is widely used in modern schooling systems and professional development to foster continuous learning in a dynamic, fast-paced world.
Key Concepts:
-
Flexible Learning: This model emphasizes learner autonomy by providing them with control over the pace, place, and mode of learning. It supports diverse learning needs and preferences by offering different ways to engage with content, whether synchronously or asynchronously.
-
Blended Learning: A blend of face-to-face and online learning, where part of the course content is delivered in-person, while the rest is available online. This approach enhances the learning experience by leveraging digital tools alongside traditional teaching methods.
- Teacher: cherotich maina


Human Resources (HR) is a critical function within organizations that focuses on the management, development, and well-being of employees. It encompasses a broad range of activities and responsibilities aimed at maximizing employee performance, ensuring compliance with labor laws, and fostering a positive workplace culture. Here’s an introduction to the key aspects of HR:
Key Functions of Human Resources
-
Recruitment and Staffing:
- Job Analysis and Design: Defining roles, responsibilities, and the necessary skills for positions within the organization.
- Talent Acquisition: Attracting, interviewing, and selecting candidates to fill job vacancies. This includes using various sourcing methods such as job postings, recruiting agencies, and social media.
- Onboarding: Integrating new employees into the organization, providing them with the necessary training, resources, and information to become productive members of the team.
-
Training and Development:
- Employee Training: Offering programs and workshops to enhance employees' skills and knowledge, ensuring they can perform their jobs effectively.
- Professional Development: Providing opportunities for career advancement and personal growth, such as leadership training, certifications, and continuing education.
- Performance Management: Evaluating employee performance through regular reviews, setting goals, and providing feedback to help employees improve and succeed.
-
Compensation and Benefits:
- Salary and Wages: Determining competitive and fair compensation structures based on market analysis, job roles, and employee performance.
- Benefits Administration: Managing employee benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and other perks. This includes negotiating with benefits providers and ensuring employees are aware of and understand their benefits.
- Incentives and Rewards: Developing programs to recognize and reward employee achievements and contributions, such as bonuses, awards, and promotions.
-
Employee Relations:
- Workplace Policies: Developing and enforcing policies that govern workplace behavior, ethics, and compliance with labor laws.
- Conflict Resolution: Addressing and resolving workplace conflicts and grievances between employees or between employees and management.
- Employee Engagement: Fostering a positive work environment that promotes job satisfaction, motivation, and retention. This includes conducting surveys, organizing team-building activities, and implementing feedback mechanisms.
-
Legal Compliance:
- Labor Laws: Ensuring the organization complies with local, state, and federal labor laws and regulations, such as equal employment opportunity (EEO), occupational safety and health (OSHA), and the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA).
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintaining accurate records of employee information, performance reviews, disciplinary actions, and compliance with legal requirements.
Strategic HR Management
- Workforce Planning: Anticipating future staffing needs and developing strategies to meet those needs through hiring, training, and succession planning.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Promoting a diverse and inclusive workplace by implementing policies and practices that support equality and respect for all employees.
- HR Analytics: Using data and metrics to assess HR performance, make informed decisions, and improve HR processes. This includes analyzing turnover rates, employee satisfaction, and recruitment effectiveness.
Trends in HR
- Technology Integration: Utilizing HR software and platforms for recruitment, performance management, payroll, and employee engagement.
- Remote Work: Adapting to the rise of remote and flexible work arrangements by developing policies and practices that support remote employees.
- Employee Well-Being: Prioritizing mental and physical health through wellness programs, mental health support, and work-life balance initiatives.
- Continuous Learning: Encouraging a culture of continuous learning and development to keep pace with changing job requirements and industry trends.
Conclusion
Human Resources is a dynamic and essential function that plays a pivotal role in the success of any organization. By effectively managing the workforce, fostering a positive work environment, and ensuring legal compliance, HR professionals help organizations achieve their goals and create a supportive, productive workplace for all employees.
- Teacher: Brenda Cherotich
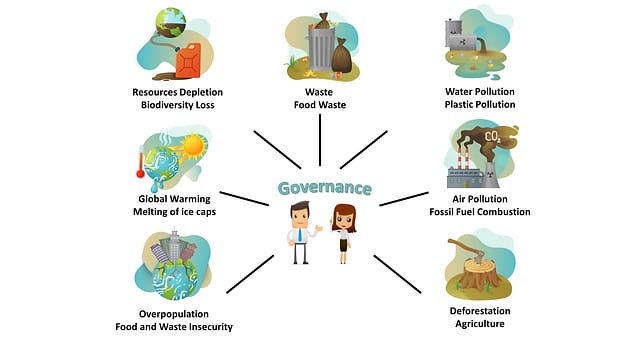

Environmental pollution refers to the introduction of harmful substances or products into the environment, causing adverse effects on ecosystems, human health, and the planet's natural processes. This pollution can take various forms, including air, water, soil, and noise pollution, and results from both natural and human activities.
Types of Environmental Pollution
-
Air Pollution:
- Sources: Emissions from factories, vehicles, burning fossil fuels, and industrial processes.
- Effects: Respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, acid rain, global warming, and ozone layer depletion.
- Pollutants: Particulate matter (PM), sulfur dioxide (SO₂), nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), carbon monoxide (CO), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and heavy metals like lead.
-
Water Pollution:
- Sources: Discharge of industrial waste, agricultural runoff, sewage, oil spills, and plastic debris.
- Effects: Contaminated drinking water, harm to aquatic life, disruption of marine ecosystems, and spread of waterborne diseases.
- Pollutants: Heavy metals (mercury, lead), nitrates, phosphates, microplastics, and pathogens.
-
Soil Pollution:
- Sources: Pesticides, industrial waste, mining activities, and illegal dumping.
- Effects: Loss of soil fertility, contamination of food crops, and disruption of soil ecosystems.
- Pollutants: Pesticides, heavy metals, hydrocarbons, and persistent organic pollutants (POPs).
-
Noise Pollution:
- Sources: Traffic, industrial activities, construction work, and urban areas.
- Effects: Hearing loss, stress, sleep disturbances, and adverse effects on wildlife.
- Pollutants: Excessive decibel levels from various human activities.
Causes of Environmental Pollution
- Industrialization: Increased production and consumption lead to the release of pollutants.
- Urbanization: Expansion of cities and infrastructure contributes to pollution through construction, waste generation, and traffic.
- Agricultural Practices: Use of chemicals, fertilizers, and pesticides leads to soil and water contamination.
- Deforestation: Reduces the earth's capacity to absorb carbon dioxide, contributing to air pollution and climate change.
- Waste Disposal: Improper disposal of industrial, household, and medical waste pollutes the environment.
Impact on Human Health and Ecosystems
- Human Health: Pollutants can cause respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and neurological disorders. Contaminated water and food can lead to gastrointestinal diseases and other health issues.
- Ecosystems: Pollution disrupts the balance of ecosystems, leading to loss of biodiversity, altered habitats, and disrupted food chains. It can cause the death of plants and animals and damage natural habitats.
Mitigation and Control
- Regulations and Policies: Implementing and enforcing environmental regulations to control emissions and waste disposal.
- Renewable Energy: Promoting the use of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydro power to reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
- Sustainable Practices: Encouraging sustainable agricultural practices, waste management, and industrial processes.
- Public Awareness: Educating the public on the effects of pollution and promoting eco-friendly practices.
- Technological Innovations: Developing and utilizing technologies that reduce emissions and waste production.
Conclusion
Addressing environmental pollution requires a collective effort from governments, industries, and individuals. By adopting sustainable practices, enforcing regulations, and raising awareness, we can mitigate the harmful effects of pollution and protect the environment for future generations.

Introduction to Project Management
Project management is the discipline of planning, organizing, and managing resources to achieve specific goals and meet specific success criteria. It involves overseeing a project from inception through completion, ensuring that it is completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
Key Concepts in Project Management
-
Project:
- Definition: A temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result.
- Characteristics: Defined start and end dates, specific objectives, and constraints such as time, cost, and resources.
-
Project Management:
- Definition: The application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet project requirements.
- Purpose: To ensure the successful completion of a project by managing its scope, schedule, costs, and quality.
-
Project Lifecycle:
- Initiation: Defining and authorizing the project. Includes creating a project charter and identifying stakeholders.
- Planning: Establishing the scope, objectives, and procedures. Includes creating a project plan, defining tasks, and scheduling.
- Execution: Implementing the project plan and performing the work defined. Involves coordinating people and resources.
- Monitoring and Controlling: Tracking project performance and making necessary adjustments. Involves controlling scope, schedule, and costs.
- Closure: Finalizing all project activities, handing over deliverables, and closing the project. Includes evaluating project performance and documenting lessons learned.
-
Key Project Management Processes:
- Scope Management: Defining and controlling what is included and excluded in the project.
- Schedule Management: Planning and controlling the project timeline.
- Cost Management: Estimating, budgeting, and controlling costs.
- Quality Management: Ensuring that the project meets the required quality standards.
- Resource Management: Planning and managing human and material resources.
- Risk Management: Identifying, analyzing, and responding to project risks.
- Communication Management: Ensuring effective communication among stakeholders.
- Stakeholder Management: Identifying and managing relationships with stakeholders.
-
Project Management Methodologies:
- Waterfall: A linear and sequential approach where each phase must be completed before the next begins.
- Agile: An iterative approach that emphasizes flexibility and customer collaboration, with regular updates and continuous improvement.
- Scrum: A subset of Agile focusing on iterative progress through sprints, with defined roles and ceremonies.
- Lean: Focuses on maximizing value while minimizing waste, often used in manufacturing and software development.
- PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments): A process-based methodology focusing on organization and control throughout the project lifecycle.
-
Project Management Tools and Techniques:
- Gantt Charts: Visual representation of the project schedule, showing tasks and their dependencies.
- PERT Charts (Program Evaluation Review Technique): Diagram that shows project tasks and their interdependencies.
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to accomplish project objectives.
- Critical Path Method (CPM): Technique for determining the longest sequence of dependent tasks and calculating project duration.
- Risk Register: Document that identifies and tracks project risks and their mitigation strategies.
-
Project Manager Role:
- Responsibilities: Leading the project team, managing resources, communicating with stakeholders, and ensuring project goals are met.
- Skills: Leadership, communication, problem-solving, negotiation, and organizational skills.
-
Success Factors:
- Clear Objectives: Well-defined project goals and deliverables.
- Effective Planning: Detailed project plan with defined tasks, schedule, and resources.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Active involvement and communication with stakeholders.
- Risk Management: Proactive identification and management of potential risks.
- Monitoring and Control: Regular tracking of project progress and making adjustments as needed.
Conclusion
Project management is essential for ensuring that projects are completed successfully, on time, and within budget. It involves a range of processes, tools, and methodologies designed to effectively manage all aspects of a project. By understanding the fundamental concepts and applying best practices, project managers can drive projects to successful outcomes and meet organizational goals.
- Teacher: Brenda Cherotich
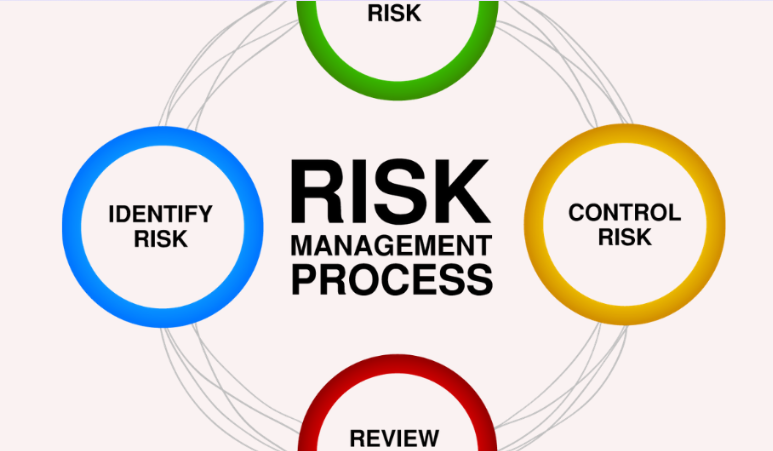
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing and controlling financial, legal, strategic and security risks to an organization's capital and earnings.
Key Components of Risk Management
-
Risk Identification: Recognizing potential risks that could affect the project or organization. This could involve brainstorming, expert interviews, and reviewing historical data.
-
Risk Assessment: Analyzing the identified risks to understand their potential impact and the likelihood of their occurrence. This often involves qualitative and quantitative risk analysis.
-
Risk Mitigation: Developing strategies and plans to minimize the impact of risks. This could include avoiding the risk, reducing the risk, transferring the risk (e.g., through insurance), or accepting the risk.
-
Risk Monitoring and Reporting: Continuously tracking identified risks, monitoring residual risks, identifying new risks, and evaluating the effectiveness of the risk management process. Regular reports should be prepared and communicated to stakeholders.
-
Risk Governance: Establishing a risk management framework and policy, assigning roles and responsibilities, and ensuring that risk management is integrated into the organizational culture.
Risk Management Process
-
Establish the Context: Define the external and internal parameters to be taken into account when managing risk, and set the scope and risk criteria for the remaining process.
-
Risk Identification: Identify where, when, why, and how events could prevent, degrade, delay, or enhance the achievement of the organization’s objectives.
-
Risk Analysis: Determine the existing controls and analyze the risk in terms of consequence and likelihood in the context of those controls. This leads to an estimation of the level of risk.
-
Risk Evaluation: Compare the estimated levels of risk against the pre-established criteria and consider the balance between potential benefits and adverse outcomes. This evaluation helps in making decisions about which risks need treatment and the priority for treatment implementation.
-
Risk Treatment: Develop and implement specific strategies to manage risk. This might involve choosing one or more options for mitigating the risk, implementing risk mitigation plans, and monitoring the effectiveness of these plans.
-
Monitoring and Review: Continuously monitor and review the risk environment, the effectiveness of the risk management strategies, and the ongoing identification and evaluation of risks.
Types of Risks
- Strategic Risks: Risks that affect the high-level goals of an organization.
- Operational Risks: Risks that affect the day-to-day operations of an organization.
- Financial Risks: Risks that impact an organization's financial standing, including market risk, credit risk, and liquidity risk.
- Compliance Risks: Risks related to the need to comply with laws and regulations.
- Reputational Risks: Risks that can affect the perception of the organization by stakeholders.
Risk Management Strategies
- Avoidance: Changing plans to circumvent the problem.
- Reduction: Taking steps to reduce the probability or impact of the risk.
- Sharing: Transferring or sharing a portion of the risk with others (e.g., insurance).
- Retention: Accepting the risk when it is outweighed by the cost of mitigating it.
Tools and Techniques
- SWOT Analysis: Assessing strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Risk Register: Documenting all identified risks, their assessment, and plans for risk management.
- Risk Matrix: Visual tool to assess the level of risk by considering the severity of consequences and the likelihood of occurrence.
- Scenario Analysis: Evaluating possible future events by considering alternative possible outcomes.
Effective risk management can help organizations minimize potential losses, increase opportunities, and achieve their objectives more efficiently.
- Teacher: Brenda Cherotich
